The Next Frontier: The Science of Human Space Exploration
"The universe is not a place for dreams confined by limits; it is a canvas for boundless possibility. Humanity's destiny is written among the stars, where our curiosity and ingenuity propel us into worlds unimagined." Freeman Dyson's vision encapsulates the spirit of exploration that drives us toward interplanetary colonization. As technology advances, we find ourselves at the cusp of an era where settling other planets is not just science fiction but an achievable goal. Here are eleven groundbreaking technologies making this possible.
11 Technologies Enabling Interplanetary Colonization
- Reusable Rockets
SpaceX’s Falcon 9 and Starship revolutionized space travel with their ability to return, refuel, and relaunch. This innovation drastically reduces costs, making regular missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond feasible. Reusability transforms interplanetary travel from a rare event to a sustainable enterprise. - Advanced Life Support Systems
NASA's Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) recycles air, water, and waste, enabling long-term human survival in space. Enhanced systems are being designed to function autonomously for years, essential for distant colonies where resupply missions are impractical. - 3D Printing for Space Construction
Additive manufacturing allows astronauts to create tools, replacement parts, and even habitats using local resources like lunar regolith. Companies like ICON are pioneering 3D-printed structures that could serve as shelters on Mars, reducing the need to transport materials from Earth. - Nuclear Thermal Propulsion
NASA and private companies are developing nuclear-powered rockets that offer faster travel times and greater efficiency than traditional chemical propulsion. These systems could cut the journey to Mars in half, reducing radiation exposure and mission costs. - Artificial Gravity Solutions
Long-term space missions face the challenge of microgravity’s harmful effects on human health. Concepts like rotating habitats or centrifuge-based spacecraft could simulate Earth-like gravity, ensuring the well-being of colonists during their journey and on alien worlds. - Energy Generation and Storage
Solar panels optimized for weak sunlight and compact nuclear reactors like NASA’s Kilopower are critical for powering habitats. These technologies ensure a steady energy supply for lighting, heating, and scientific experiments, even in environments with limited sunlight. - Autonomous Robotic Assistants
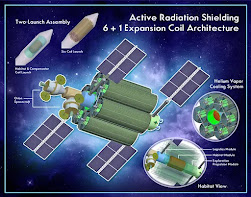
Robots such as NASA’s Perseverance rover pave the way for human exploration by scouting terrain, gathering data, and preparing sites for human arrival. Future robotic assistants will build infrastructure, extract resources, and assist with daily tasks, reducing human workload. - Radiation Shielding Innovations
Cosmic radiation poses a major risk to spacefarers. Advances in shielding, such as water-based barriers, magnetic fields, and regolith-covered habitats, protect colonists from harmful radiation, ensuring their safety during extended stays. - In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU)In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) is a key NASA strategy aimed at enabling sustainable space exploration. It involves harnessing and converting local resources such as lunar or Martian regolith, ice, or atmospheric gases into usable materials like oxygen, water, fuel, and building components. By reducing reliance on Earth-supplied materials, ISRU significantly lowers mission costs and increases mission duration and resilience. Technologies under development include oxygen extraction from regolith and water electrolysis from ice deposits. ISRU is essential for future Moon and Mars missions, supporting habitats, life support systems, and propulsion needs, thereby paving the way for long-term human presence beyond Earth.
Interplanetary Internet
Reliable communication is essential for colonization. NASA’s development of the Delay/Disruption-Tolerant Networking (DTN) protocol ensures data can be transmitted across vast distances, enabling coordination, research, and even remote control of robotic operations.- Bioengineered Crops for Space
Genetically modified plants designed to grow in low-gravity and nutrient-poor soils will sustain life off-world. These crops provide food, oxygen, and waste recycling, transforming barren landscapes into life-supporting ecosystems.














No comments:
Post a Comment